
A solid foundation in cybersecurity is crucial for individuals aiming to excel in today’s rapidly expanding digital world. Aspiring cybersecurity professionals often face a critical decision: Which certification path should they pursue?
The CISSP and CySA+ certifications are two common options. Both credentials offer distinct advantages and cater to different career goals. In this article, we will explore the eligibility criteria, exam formats, and potential career paths associated with CISSP and CySA+. This information will assist you in determining which certification is best suited to your cybersecurity career objectives. By considering the key elements that differentiate these credentials and align with your interests, expertise, and long-term professional goals, you can make an informed decision and choose the most appropriate route.
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
The CISSP certification is widely recognized as a prestigious validation of expertise for security professionals. It encompasses ten key areas, including access control systems, business continuity planning, disaster recovery planning, physical security, operations security, management practices, and telecommunications and network security.
Attaining the CISSP credential is a noteworthy achievement that demonstrates a professional’s capability to design, implement, and maintain robust cybersecurity programs with confidence and reliability.
If you are preparing for the exam, we recommend trying out the free CISSP Practice Exam to increase your chances of passing on your first attempt.
CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst (CySA+)
The CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst (CySA+) certification evaluates candidates’ knowledge and skills in detecting and analyzing indicators of malicious activity, understanding threat intelligence and management, responding to attacks and vulnerabilities, performing incident response, and effectively reporting and communicating relevant activities. The CySA+ certification underwent an update in June 2023, introducing the test code CS0-003.
What distinguishes the CySA+ certification from others is its focus on security analytics, which provides a deeper understanding of this field. Specifically, this certification delves more extensively into analytics. The CySA+ test objectives cover the following topics:
-
Security Operations
-
Vulnerability Management
-
Incident Response and Management
- Reporting and Communication
Comparison of CISSP vs CySA+
Prerequisites

CISSP
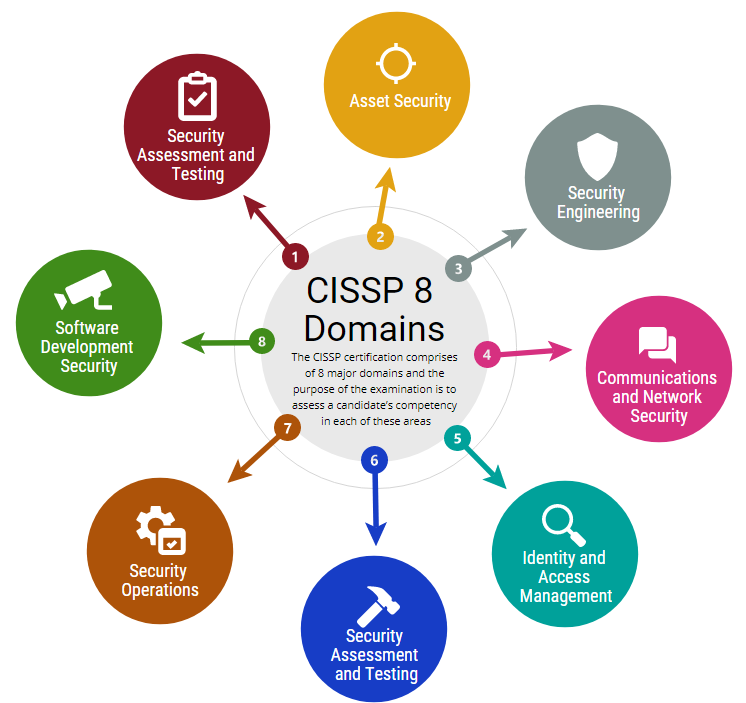
Individuals aspiring to obtain the CISSP certification must possess a minimum of five years of paid work experience in at least two of the eight domains covered by the CISSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK):
- Security and Risk Management
- Asset Security
- Security Architecture and Engineering
- Communication and Network Security
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Security Assessment and Testing
- Security Operations
- Software Development Security
If a candidate holds a four-year college degree, a regional equivalent, or an additional certification from the (ISC)² recognized list, it can fulfill one year of the required experience for the CISSP certification. In the case of educational credit, just one year of experience is sufficient. Candidates who lack the necessary five years of experience for the full CISSP certification can still take the CISSP exam to become an Associate of (ISC)². Similar to the CCSP certification, associates have six years to fulfill the requisite five years of experience.
CySA+
Individuals from diverse backgrounds and varying experience levels in IT and cybersecurity choose to take the CompTIA CySA+ exam. While there are no specific prerequisites for the CySA+ certification, it is recommended to have a minimum of four years of hands-on experience in information security or related fields before attempting the exam.
The CySA+ certification is designed to be pursued after completing the CompTIA Security+ certification or gaining equivalent experience, with a focus on technical and practical aspects. The extent and quality of your prior experience in cybersecurity and analysis play a significant role in bridging the knowledge gap between your current understanding and the expected knowledge for the certification.
Exam Factors
CISSP
Regarding the CISSP exam, it is a three-hour exam that requires a minimum score of 700 out of a possible 1000 points to pass. The exam fee for CISSP is $749.
The exam underwent a recent update on April 15, 2024, which adjusted the domain weights of some of the exam’s content areas. These updates were based on the most recent Job Task Analysis (JTA) conducted by (ISC)². The examination weights across the eight CISSP domains are as follows:
- Security and Risk Management: 16%
- Asset Security: 10%
- Security Architecture and Engineering: 13%
- Communication and Network Security: 13%
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): 13%
- Security Assessment and Testing: 12%
- Security Operations: 13%
- Software Development Security: 10%
The number of questions in the CISSP exam can vary from 125 to 150, consisting of a blend of multiple-choice and “advanced innovative items” that involve drag-and-drop style questions. It is important to note that these questions do not require written answers. The CISSP exam is available in English, Chinese, German, Japanese, and Spanish.
CySA+
CompTIA CySA+ stands out as the only intermediate high-stakes cybersecurity analyst certification that includes performance-based questions. The exam comprises a maximum of 85 questions and allows a duration of 165 minutes to complete. The question types encompass multiple-choice, and performance-based questions. Multiple-choice questions are further categorized as single- and multiple-response options. The performance-based items evaluate your problem-solving skills in a simulated environment.
The CySA+ test covers four domains that align with the core responsibilities of a cybersecurity analyst:
- Security Operations: 33%
- Vulnerability Management: 30%
- Incident Response Management: 20%
- Reporting and Communication: 17%
The focus is on monitoring and identifying vulnerabilities that arise from insecure systems and software, regardless of programming language, while effectively responding to threats. For example, a performance-based question might require you to plan, install, configure, monitor, and analyze an intrusion detection system (IDS) or SIEM. Analyzing the output of such tools to determine threats is an example of the practical scenarios you may encounter. Other questions may pertain to continuous monitoring activities such as log reviews, impact analysis, and response.
CompTIA certification exams are conducted under proctored conditions at secure Pearson VUE testing centers. CySA+ is an advanced security analyst certification that addresses advanced persistent threats within the cybersecurity landscape post-2014. While the passing score for the CySA+ certification exam may vary across exam versions, it is typically set at 750 on the 100-900 scale.
Successful candidates often find that following a structured study program, consisting of a few hours each day over an extended period of time, is beneficial. There are many CySA+ Practice Tests available online.
Job Roles
CISSP
(ISC)² upholds its responsibility to members by ensuring the continued relevance of the CISSP certification. The Job Task Analysis (JTA) is a comprehensive and critical process that identifies the tasks performed by security professionals in the CISSP field. The findings from the JTA process are used to continuously update the exam content. This ensures that candidates are assessed on topics that align with the current responsibilities and duties of information security professionals in practical scenarios.
The CISSP certification is intended for experienced security practitioners, managers, and executives who aim to showcase their expertise in a broad range of security principles and techniques. Typical job titles associated with CISSP certification include:
- Chief Information Security Officer
- Chief Information Officer
- Director of Security
- IT Director/Manager
- Security Systems Engineer
- Security Analyst
- Security Manager
- Security Auditor
- Security Architect
- Security Consultant
- Network Architect
CySA+
The CompTIA CySA+ certification provides professionals with the knowledge and skills required for cybersecurity positions such as:
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Incident Response Analyst
- Threat Hunter
- Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst
- Vulnerability Management Analyst
- Cybersecurity Engineer

Which Should You Choose Between CISSP vs CySA+?
Identifying Personal Career Objectives and Aspirations
The CISSP certification could be the ideal choice for you if you aspire to advance to senior-level or managerial positions in cybersecurity and possess a comprehensive understanding of information security management. The CISSP certification encompasses a wide range of security issues and is widely recognized in the industry as a symbol of competence and expertise. It demonstrates your ability to develop and implement robust security plans while effectively managing security risks.
On the other hand, the CySA+ certification may be a better fit if you wish to concentrate exclusively on threat detection, response, and vulnerability management, and are interested in hands-on technical roles such as cybersecurity analysts or incident responders. CySA+ focuses on practical skills such as identifying and managing security threats, responding to incidents, and conducting vulnerability assessments. It provides a solid foundation for professionals who want to directly engage with security operations teams.
Assessing Existing Knowledge and Experience
The CISSP certification is recommended for individuals with a minimum of five years of full-time work experience in two or more domains, such as security operations, risk management, or network security. If you already possess a strong understanding of information security and have worked in various security domains, obtaining the CISSP certification can enhance your career prospects. It demonstrates your capability to develop comprehensive security strategies while providing a holistic view of security management.
On the other hand, the CySA+ certification is more accessible to individuals with less work experience or those who are starting out in their cybersecurity careers. While a basic understanding of cybersecurity principles is still essential, it is a viable option for professionals seeking hands-on technical experience. The CySA+ certification emphasizes practical skills in threat detection, response, and vulnerability management. If you have previous experience or a keen interest in areas such as incident response, security operations, or vulnerability assessments, CySA+ can help you enhance your technical abilities and unlock opportunities for specialized roles within cybersecurity operations teams.
Considering Job Market Demands and Requirements
The consideration of job market demands and requirements is crucial when deciding between CISSP and CySA+ certifications. Examining job postings and industry trends can provide insights into which certification holds more value in the specific region or industry you are targeting.
For instance, if you notice a significant number of job postings that emphasize the CISSP certification as a prerequisite or highly desirable qualification, it indicates a strong demand for professionals with CISSP expertise in the job market. In such cases, obtaining the CISSP certification may give you a competitive edge and increase your chances of securing certain positions, particularly those focused on information security management, policy development, and leadership roles.
On the other hand, if you find that many organizations are seeking professionals with practical skills in threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management, you may discover a higher demand for the CySA+ certification. This suggests that acquiring the CySA+ certification could position you well for technical roles that involve hands-on security analysis and incident handling.
FAQs

How many people pass the CISSP?
If you hold this cybersecurity course certificate, you will be regarded as one of the most sought-after candidates by numerous employers. Passing this exam is challenging, which is why thorough preparation is essential. However, on average, 50% to 60% of individuals who take the exam successfully pass it.
How can I earn the CISSP certification?
- 5 Years Experience: You need a minimum of 5 years of cumulative paid full-time work experience in two or more of the 8 domains of the (ISC)² CISSP CBK®. Candidates may be eligible for a one-year experience waiver if they hold a 4-year college degree, regional equivalent, or an additional credential from the (ISC)² approved list.
- Schedule the Exam and Complete the Examination Agreement: You will need to schedule your exam with Pearson VUE, submit the exam fee (or provide your pre-purchase voucher information, if applicable), and complete the Examination Agreement.
- Pass the Exam: Achieving a passing score on the CISSP examination requires a scaled score of 700 points or greater.
- Get Your Endorsement: Once you have been notified that you have successfully passed the exam, you will need to subscribe to the (ISC)² Code of Ethics and have your application endorsed. The endorsement must come from an (ISC)² active member who is a certified professional.
- Maintain the CISSP Certification: To maintain your CISSP certification, you must re-certify every 3 years.
Is the CySA+ certification worth it?
This credential can help individuals advance their careers in various relevant professions and is also recognized as one of the DoD’s baseline qualifications, further enhancing its value. The certification validates the individual’s knowledge and is widely recognized and respected in the cybersecurity industry.
Will CySA get you a job?
Can I skip CompTIA Security+ and go straight to CompTIA CySA+?
Conclusion
Both CISSP and CySA+ certifications offer valuable benefits for a career in cybersecurity, but their suitability depends on individual goals and aspirations. The CISSP certification provides a broader and more comprehensive understanding of information security management and is widely recognized as a symbol of expertise and professionalism. It is ideal for professionals seeking senior-level positions or managerial roles in cybersecurity. On the other hand, the CySA+ certification focuses specifically on threat detection, response, and vulnerability management, making it a solid choice for individuals interested in hands-on technical roles such as cybersecurity analysts or incident responders.
Ultimately, the decision between CISSP and CySA+ should be based on personal career objectives, current skill set, and the specific demands of the desired job market. Making an informed decision, guided by careful consideration of these factors, will lead to a certification that aligns with individual aspirations and paves the way for a successful and fulfilling career in cybersecurity.

PCCN vs CCRN: Which Certification Should I Take?
In this discussion, we will examine the fundamental distinctions between PCCN vs CCRN certifications, allowing you to make an informed and right decision about which certification is best for your nursing career progression.
June 20, 2023

Is PCCN Worth It? A Comprehensive 2024 Study Guide
In this article, we will provide all the enrollment criteria, how to apply, whether is PCCN worth it for you to obtain, and how to get a high mark.
June 20, 2023

PCCN Requirements - How to Become a Progressive Care Certified Nurse?
To become a progressive care nurse, you must first obtain the PCCN certification. This post will help you understand PCCN certification, PCCN requirements, and efficient approaches to obtaining this certification.
June 20, 2023
