An EMT or paramedic career may be the best fit for you if you’re interested in a profession that involves saving lives. What these jobs entail and how they differ from one another will be explained in this blog post. We will also discuss the certification requirements so that you can begin your path to this fulfilling career.
The level of education and patient care are the two main differences when it comes to EMT vs Paramedic. An EMT cannot give the same degree of treatment for patients as a paramedic, who often has greater training.
What are they?
EMTs are also known as Emergency Medical Technicians, they are the person who will be providing pre-hospital care and who are typically the first person on the scene.
Paramedics, also known as Emergency Medical Technicians with Advanced Life Support training, have more advanced skills than an EMT, such as suturing wounds and administering IV drugs. They can provide both basic and advanced life support services for patients in emergency situations.
Where do they work?
Some places where EMTs can often work are ambulance services, governments, hospitals, fire departments, and hospital departments. In these places, a medical director or physician supervises their work and they have a limited scope of practice.
On the other hand, Paramedics most commonly are employed by emergency medical services (EMS). There, they can work with EMTs, but the number of Paramedics is often larger than EMTs. Besides, Paramedics can also work for air ambulances and fire services.
Maybe you care about the salary of an EMT.
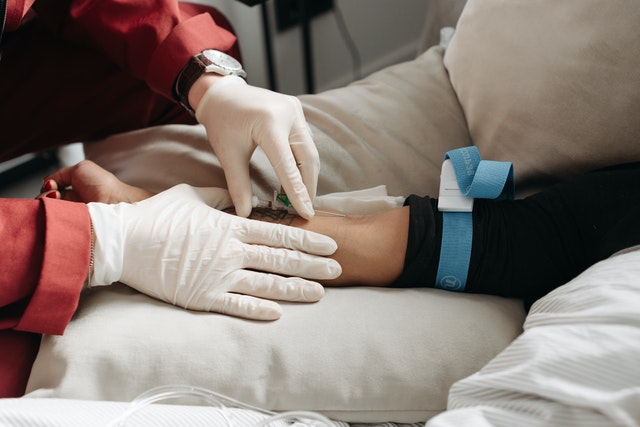
The difference in typical responsibilities between EMT vs Paramedic
As the first responders to an emergency situation, EMTs have some duties such as responding to 911 calls for emergency medical technicians, assessing patients, helping them stabilize, and treating them on the way to hospitals or between facilities. Some of the treatments they can do within their scope of practice are using a backboard and restrains to keep the patients still and safe in the ambulance during transport, providing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), bandaging wounds, and controlling external bleeding, preventing shock and further injury in patients. They also must maintain patient records, and inform the hospital about the injury or illness, the number of patients being transported, and the expected time of arrival.
In addition to some EMTs’ basic duties, Paramedics can take more advanced practices. For instance, they might provide additional treatment to the patient during transport, such as intravenous (IV) medications or fluid replacement. They can also use more advanced equipment in order to treat patients who have been injured severely enough that they need surgery and are transported by helicopter.
Education and experience requirements
If you want to become an EMT, having a high school diploma or GED is sufficient. You do not need an associate’s or bachelor’s degree. However, completing an EMT training program that is offered by community colleges and vocational schools is a must. Such programs often are completed in 150 hours. In addition, to become a successful EMT, students must also pass the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) cognitive exam.
The highest level of EMTs is Paramedics which is why becoming a Paramedic requires more education than becoming an EMT. Students must finish basic and advanced EMT training courses and additional studies. Generally, they also have to work as EMTs for one to two years to gain experience. Students must also take EMT courses at a college or university. These programs typically last between two and four years. That depends on the school’s curriculum, which ranges from 100 to 200-course hours. Paramedics are required to be certified by the National Board for Certification of Emergency Medical Technicians (NBCET).
You can get more about NREMT Skills Sheets in our blog.
Certification and license
Obtaining CPR certification is a must for anyone who wants to become an EMT because only a person who possesses CPR certification can enroll in an EMT training program. Many organizations provide students with that certification such as the American Red Cross and the American Heart Association. Another certification students must take to become an EMT is the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) certification. NREMT certification is the guarantee of a student’s competence and almost every state requires it for becoming a licensed emergency medical technician. The EMT must be at least 18 years old and should have a valid driver’s license to receive an NREMT license.
In order to become a Paramedic, you are required to obtain all the licenses as an EMT. In addition, Paramedics must pass the NBCET Exam and also be licensed by their state. The National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) administers this exam which is a two-part assessment that consists of an essay test and a computerized practical examination where students are required to perform skills such as cardiac monitoring, and intravenous fluid administration, and airway management.
How do you become an EMT?
Steps for Becoming an EMT:
- 18 years old or older with a valid driver’s license.
- Complete your basic educational requirements – a high school diploma or GED.
- Gain CPR certification from the American Red Cross or the American Heart Association.
- Take the NREMT exam and get your certification once you pass it.
- You can take boot camp to become certified but this is not mandatory in most states. This usually takes about three weeks).
To get more information about the way to become an EMT, you can try to visit our blog.
How do you become a paramedic?
You have to meet the following requirements:
- 18 years old or older with a valid driver’s license.
- Complete your basic educational requirements – a high school diploma or GED.
- Gain CPR certification from the American Red Cross or the American Heart Association if you want to work as an EMT and not be limited to just paramedics (this usually takes about three weeks).
- Take the NREMT exam and get your certification once you pass it.
- Get a job as an EMT for at least two years. This will give you more experience in emergency medical situations.
- Complete paramedic school (this usually takes about six months).
Visit our blog if you are interested in how to become a paramedic.
In short, a paramedic has greater training than an EMT, which is the main distinction between the two professions. A paramedic administers basic life support (BLS), along with advanced cardiac care, including giving patients medicines and conducting endotracheal intubation (EIT).
We advise using our free EMT practice test if you plan to take the EMT-B exam. You may prepare for your upcoming exam to the fullest extent possible with the help of thousands of free EMT practice questions and our innovative gamified learning approach. Take it!

PCCN vs CCRN: Which Certification Should I Take?
In this discussion, we will examine the fundamental distinctions between PCCN vs CCRN certifications, allowing you to make an informed and right decision about which certification is best for your nursing career progression.
June 20, 2023

Is PCCN Worth It? A Comprehensive 2025 Study Guide
In this article, we will provide all the enrollment criteria, how to apply, whether is PCCN worth it for you to obtain, and how to get a high mark.
June 20, 2023

PCCN Requirements - How to Become a Progressive Care Certified Nurse?
To become a progressive care nurse, you must first obtain the PCCN certification. This post will help you understand PCCN certification, PCCN requirements, and efficient approaches to obtaining this certification.
June 20, 2023



![The Ultimate Chemistry Study Guide For HESI A2 Exam [2024]](https://passemall.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/chemistry-study-guide.jpeg)